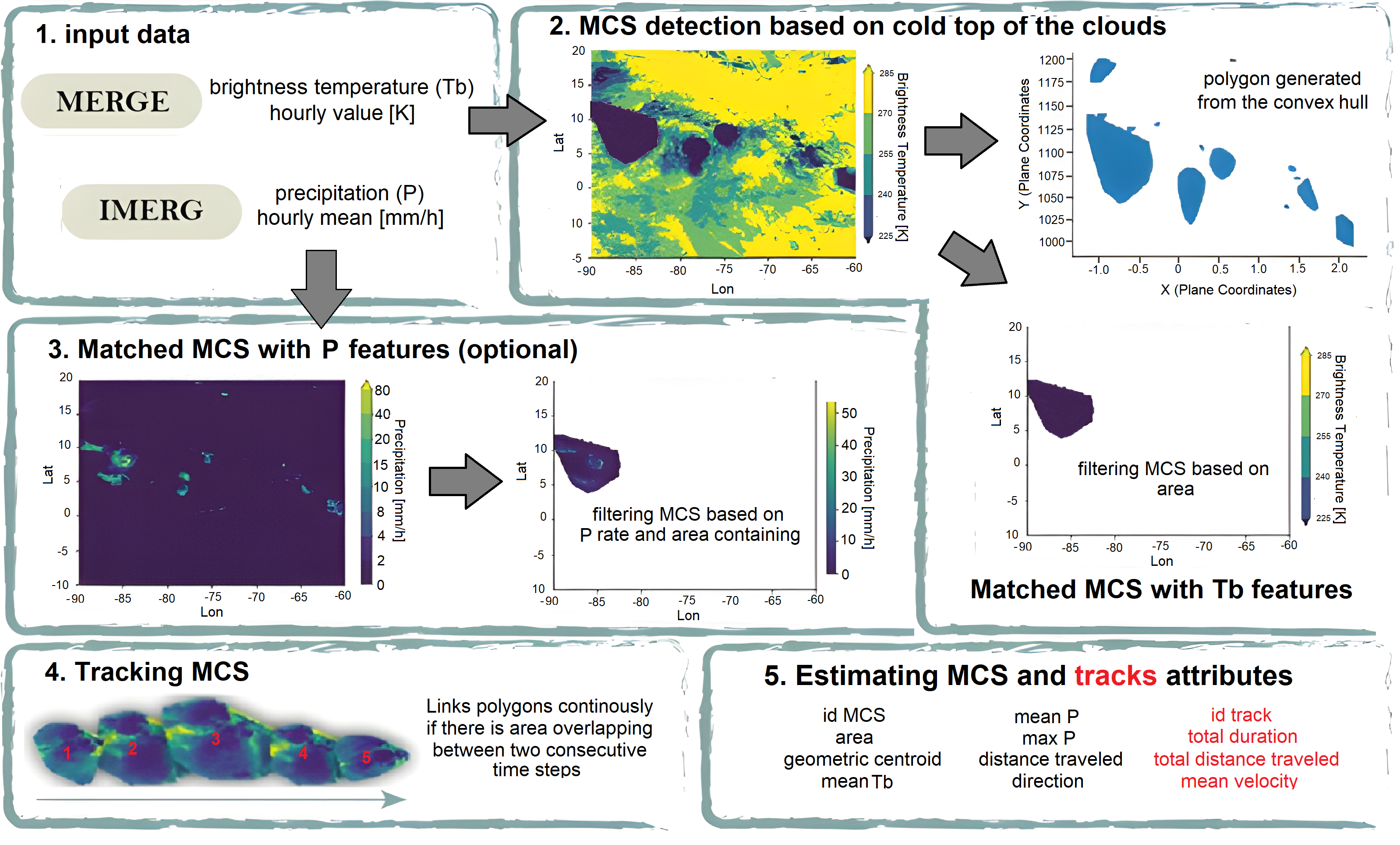
ATRACKCS

The Algorithm for TRACKing Convective Systems (ATRACKCS, Robledo et al. (2024)) is an open access Python package for the detection and tracking of MCSs.
In MCSMIP, MCS detection and characterization are performed using these steps:
-
At a given time step, the algorithm identifies cold cloud systems using a predefined Tb threshold and converts them into polygons. In this case Tb <= 241 k.
-
Transform from geographic to plane coordinates and compute an approximate area of the defined region, discard all regions where area is <= 5000 km^2.
-
Apply a buffer of 0.1 to each identified polygon and merge those overlapping, ensuring the algorith treats these systems as a single entity.
-
Estimate precipitation attributes of the identified systems and discard systems that do not meet a minimum precipitation rate of 4 mm h-1 in at least five pixels within the system.
-
Tracking: To assign different polygons to the same track in time, ATRACKCS uses a predefined threshold of overlapping area in consecutive times. The minimum area overlapping allowed is 25%. To deal with the splitting and merging of systems, if multiple systems overlap at the same timestep, ATRACKCS evaluates which systems satisfy the identification criteria and then selects the one with the higher overlapping area to the previous time step to continue the track; the remaining systems are tracked as new ones if satisfy the thresholds.
ATRACKCS can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7025989.
Reference
- Robledo, V., Henao, J. J., Mejía, J. F., Ramírez‐Cardona, Á., Hernández, K. S., Gómez‐Ríos, S., & Rendón, Á. M. (2024). Climatological tracking and lifecycle characteristics of mesoscale convective systems in Northwestern South America. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres,129, e2024JD041159. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD041159